Planning Notes
For the design of filtering separators, a wide variety of information is required for the dimensioning, design, mode of operation and choice of materials:
- The type of plant, process, apparatus or machine
-
The mode of operation of the filter system (continuous or discontinuous)
- The properties of the gas (e.g. hazardous to health, flammable or corrosive)
- The properties of the particles (e.g. hazardous to health, flammable, hygroscopic, caking or agglomerating)
- The properties of the gas/dust mixture (e.g. explosive)
Design checklist
- Installation site above sea level in m
- Information about the gas to be cleaned
- Flow rate m3/h
- Temperature °C
- Composition (e.g. volume fractions)
- Moist g/kg dry air
- Water dew point (possibly acid dew point) °C
- Density kg/m3
- Pressure of the gas at the entrance to the separator hPa
- desired clean gas dust concentration mg/m3
- Information about the particles
- Average concentration in raw gas g/m3
- Maximum concentration in raw gas g/m3
- particle size distribution
- Density g/cm3
- Bulk density g/cm3 or t/m3
- Composition according to material components, based on dry substance % mass fraction
Flow rate (Q)
The basis for the design of filtering separators is knowledge of the volume flow to be cleaned. This is either process-related or dependent on the conditions of the extraction (e.g. dust protection at the workplace).
Important influencing factors are:
-
temperature
-
Print
-
gas atmosphere
-
Properties of the dust material to be separated and its concentration
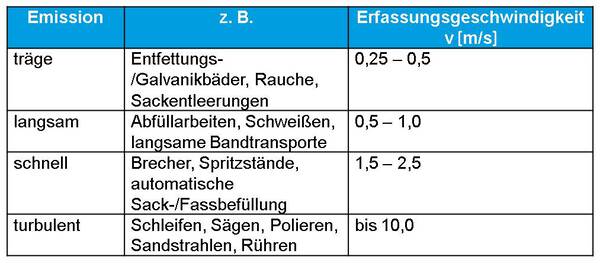
A starting point for determining air quantities is the so-called acquisition speed at open surfaces, inlet openings, hoods and machine cladding
Q [ m 3 /min ] = F [ m 2 ] xv [ m/s ] x 60
Determination of the required filter area
As a first approximation, the size of the required filter can be determined using the following equation:
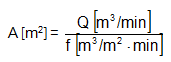
Q = volume flow of the permeated gas
A = extension filter area
f = specific filter surface load
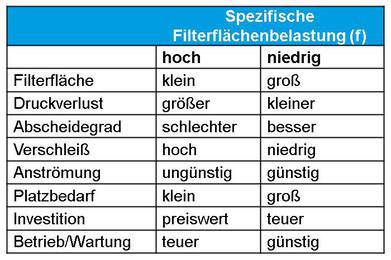
filter surface loading
An essential parameter of the filtering separator is the filter surface load. The filter surface load is generally between 0.5 m 3 /(m 2 min) and 2.5 m 3 /(m 2 min), but in individual cases it can also be significantly higher. Usual pressure differences are in the range of 400 Pa to 1,500 Pa. These areas are determined by the aspects:
-
filter medium
-
service life
-
Investment and operating costs
-
space requirement
-
operational reliability
-
clean gas dust content
Parameters influencing the filter surface load
Properties of the particles to be separated (e.g. particle size distribution, agglomeration behavior):
-
raw gas dust content
-
targeted clean gas dust content
-
Desired pressure loss of the system
-
desired service life of the filter medium
-
Gas composition (especially moisture content)
-
Type of separator / space requirement
-
regeneration procedure
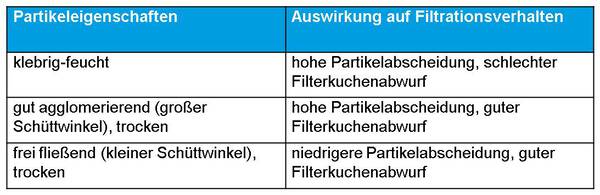
Estimation of the filter surface load according to Flatt
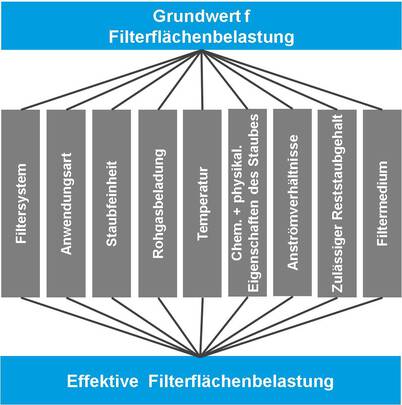
Typical filter surface loads
Typical filter surface loads for filtration separators with pressure surge cleaning
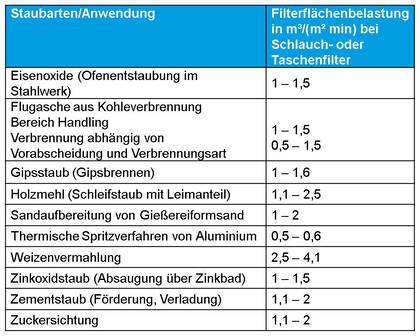
Specific filter surface load
The specific filter surface load influences the effectiveness and the degree of separation of the dust extractor.